Bioprinting
3D bioprinting is revolutionizing tissue engineering and the future of health. BICO's Bioprinting business area provides the most cutting edge technologies, to the brightest minds, to enable this future.
On this page
What is Bioprinting?
What is Bioprinting?
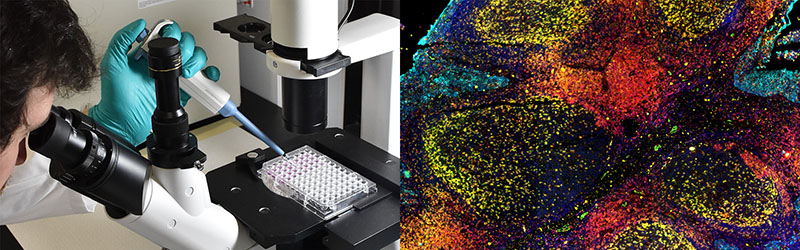
Bioprinting is an additive manufacturing process similar to conventional 3D printing – it uses a digital file as a blueprint to print an object in a variety of geometries and sizes. But unlike 3D printing, bioprinters print with cells and biomaterials, creating organ-like structures that mimic physiological conditions
Why Bioprinting?
Bioprinting has massive potential to revolutionize the fields of tissue engineering, drug discovery and regenerative medicine. Bioprinted tissue enable researchers to test potential treatments and evaluate efficacy in earlier stages, and providing a more realistic model of cellular function. In time, new drugs and treatments can be developed following a process designed to minimize failures, reduce animal testing and reach clinical trials faster.
Bioprinting helps address the major challenge faced by cell biologists around the world. The challenge of recapitulating the in vivo environment. By controlling both macro and micro features, bioprinters enable researchers to fine tune geometries, cell positioning, biomechanical gradients and many more parameters that provide the ideal biological environment for cells to thrive.
Applications of Bioprinting
Unfortunately, 21 patients per day die due to organ transplant shortages. Being able to bioprint organs could help clinicians keep up with patients or eliminate the list entirely. While this solution is far down the line, it is one of the most impactful possibilities in the field.
Customer Spotlights

Treatments for knee injuries with 3D bioprinted cartilage
A research group at Gothenburg University has developed an in-depth understanding of stem cells, and how they can be reprogrammed to create life changing therapies.

Redefining Personalized Medicine with Bioprinted Cartilage Grafts
CELLINK’s INKREDIBLE+™ bioprinter and Advanced BioMatrix’s LifeInk® 200 type I collagen were used in a groundbreaking nasal cartilage bioprinting study recently published in the Journal of Tissue Engineering.
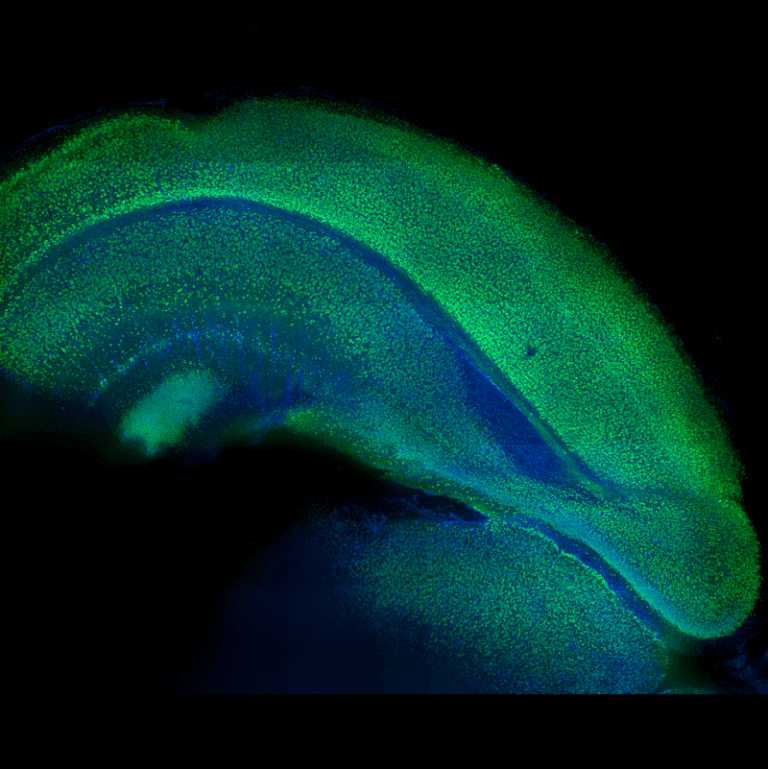
Potential treatment for degenerative muscle disorders
Researchers at Johns Hopkins University conducted a study on the human stem cells potential use as a treatment for degenerative muscle disorders.
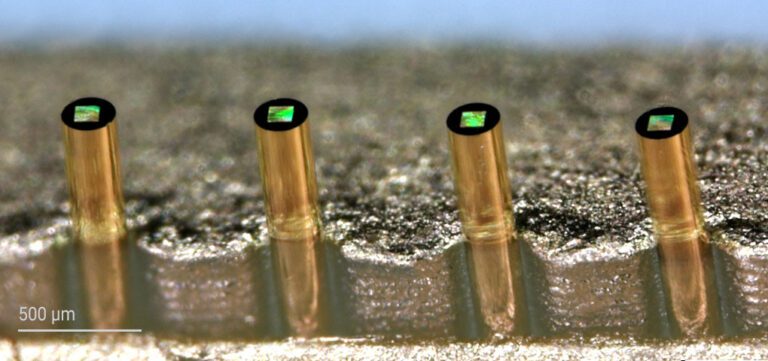
On-fiber printed sensor for label-free detection of bacteria to prevent antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is one of the greatest threats to global health, food safety and development. With this in mind, researchers of the Imperial College London developed a novel fiber-optics Raman spectroscopy sensor for the label-free identification of bacteria.

3d Bioprinted Human Skin – The Future of Cosmetic Testing
CTIBiotech, an innovative R&D firm based in Lyon, France, is using CELLINK’s BIO X 3D bioprinter to produce in vitro full skin models from human cells.

On-demand Bioprinted Patient-specific Heart Tissue minimizing the risk of transplant rejection
University of Technology in Sydney is developing bioprinted heart tissue on demand with patient-specific cells to minimize the risk of transplant rejection.

Mass Produced Stem Cells – A Gateway to Personalized Medicine
Ronawk mass-produces adult stem cells using bioprinters from CELLINK paving the way for the possibility to grow and transplant patients’ own stem cells without the need for the immunosuppressive drugs that are usually required after an organ donation.

More relevant alternative to testing women’s personal care products on animals.
Good Clean Love is advocating for the use of a 3D model of human tissue developed by MatTek as a more relevant alternative to testing women’s personal care products on animals.
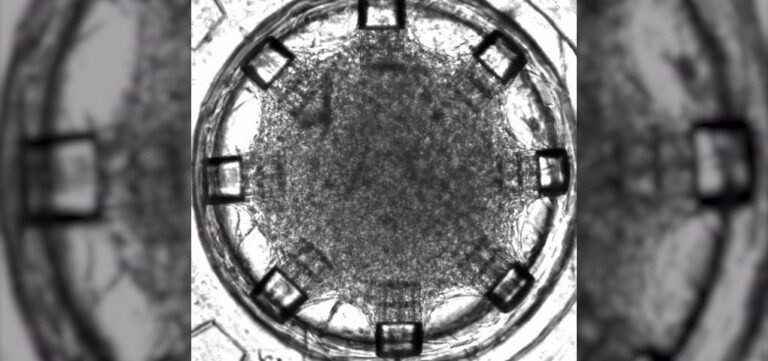
One step closer to implantable heart patches driving research on cardiac diseases and drug delivery
Researchers from Boston University have manufactured a microfluidic heart-on-a chip platform, a model of a human heart, paving the way for fundamental studies of heart tissue and eventually enables the fabrication of tissue that can be implanted into the beating heart

More Efficient Delivery of Chemotherapy to Cancerous Brain Tumors
Cornell Medical College is developing nanomaterials to more efficiently deliver oncology drugs to the brain, eliminate cancerous tumors and, ultimately, improve the survival rate of patients with DIPG tumors among other brain cancers.
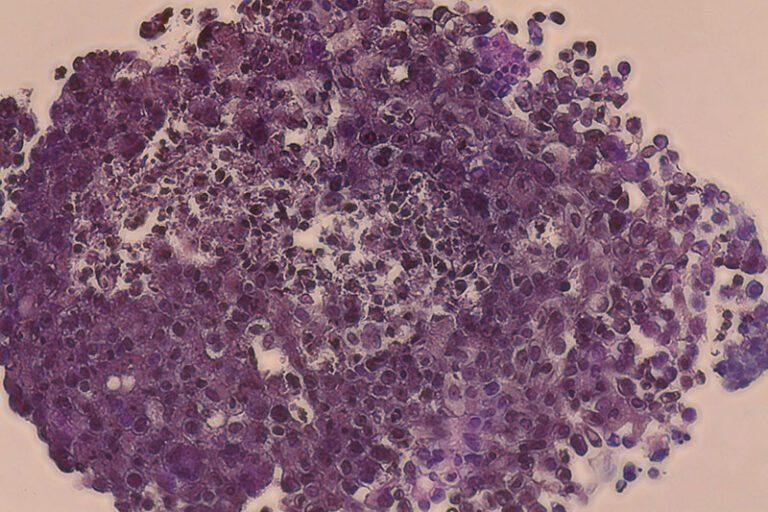
Patient-specific tumor models for individualized drug testing
Carcinotech bioprints patient-specific test models with cells from biopsy samples and has benefited greatly from CELLINK’s expertise in the field.
Publications
Companies
By releasing the first universal bioink in 2016, CELLINK democratized the cost of entry for researchers around the world and played a major role in turning the then up-and-coming field of 3D bioprinting into the thriving $1 billion industry it is today. CELLINKs bioinks, bioprinters, software and services have enabled critical breakthroughs in a wide range of applications from 3D cell culturing to tissue engineering to drug development.
The world leader of reliable in vitro human tissue model innovation. MatTeks skin, ocular, oral, respiratory, and intestinal tissue models are used to assess safety and efficacy throughout the cosmetics, chemical, pharmaceutical, and household product industries. These advanced tissue models empower companies to achieve their goals of non-animal testing while lowering testing costs and providing human-relevant results.
With over 2,500 users, Nanoscribe develops and produces 3D printers and maskless lithography systems for microfabrication as well as specially developed printing materials and application-specific solution sets. The specialist for additive manufacturing of high-precision structures and objects on the nano-, micro- and mesoscale was founded in 2007 as a spin-off of the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT).
A pioneer in the field of Digital Light processing (DLP) based printing is an emerging force within the Bioprinting industry. Allegro 3D’s DLP based bioprinting technology enables high-throughput manufacturing of biomedical devices, and precision human tissues for cell culture, drug screening, and regenerative medicine applications.
Featured Product Offering
With six printheads in total for unparalleled versatility, the BIO X6 bioprinter from CELLINK makes it easier to produce more complex and sophisticated constructs with a broader range of materials, cells and crosslinking tools. With many possible combinations, the six slots significantly increase throughput, cut down on print time and improve experiment efficiency. The BIO X6 is the preferred system for researchers seeking to enhance 3D cell culturing, tissue engineering, disease modeling and drug screening applications.
MatTek’s patented EpiDerm system is a leading in vitro testing technology for dermal toxicologists and formulation scientists. With multiple ECVAM validations and OECD accepted test guidelines, EpiDerm is a proven in vitro model system for chemical, pharmaceutical and skin care product testing.
The highest density collagen ink available on the market from Advanced Biomatrix, tailored for effortless bioprinting. Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body making it the premier material for developing bioprinted constructs with in vivo like conditions.
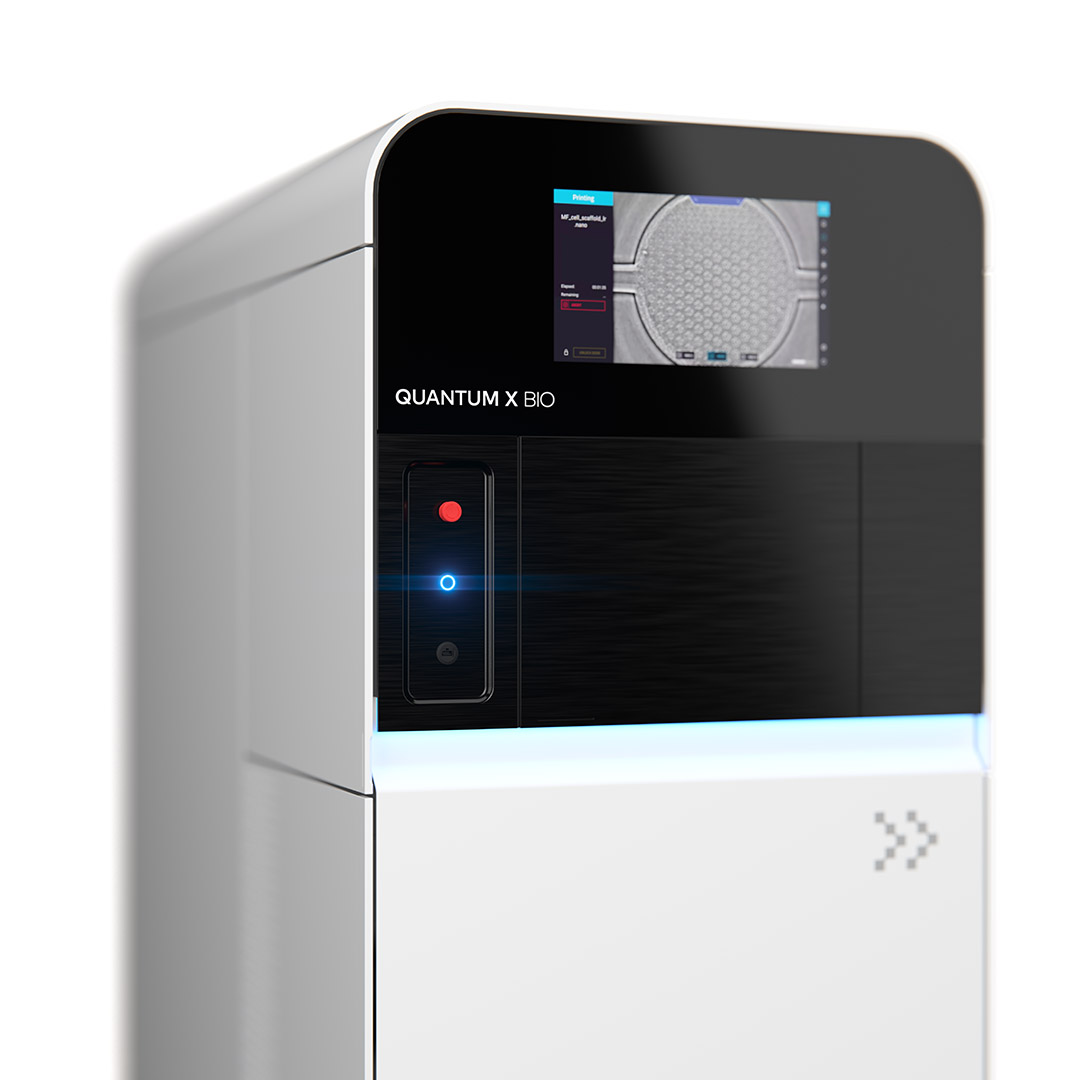
The Quantum X bio, a true demonstration of bioconvergence. A product that is co-developed by CELLINK and Nanoscribe, it is the first of its kind 3D bioprinter, enabling submicron printing resolution, and raising the bar for high precision 3D bioprinting. Powered by Two Photon Polymerization (2PP), the system is the premier tool for miniaturizing bioprinting, redefining what it means to work within advanced biomedical applications, including tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Further Reading
3D Bioprinting Set To Propel Medical Research Forward
3D printing techniques are being used in medical research to establish more personalized treatment approaches and accelerate drug discovery. The technology is unlocking the potential of 3D cell culture approaches to better replicate the human body, gain a greater understanding of various cell types and, ultimately, develop patient- and organ-specific treatment pathways.
How 3D Bioprinters Are Advancing Cancer Research
Although the past decade has yielded significant reductions in the cancer death rate around the world, cancer is still the second leading cause of death globally, accounting for about 10 million deaths in 2020. This sobering statistic makes the search for more efficient cancer solutions an important priority for researchers the world over. While animal models have advanced our understanding of the molecular mechanisms associated with cancer and its progression, therapeutics developed with these interspecies models often fail in clinical trials because the efficacy results do not translate to humans.
Fighting to End Animal Testing
Drug and cosmetic developers are still mandated to test on animals, even if it doesn’t benefit the science. This leads to the experimentation on and death of hundreds of millions of primates, dogs, rabbits, mice and other animals. With 3D bioprinting, BICO is replacing outdated methods for drug discovery to end animal testing once and for all.